Learn what is data integration, why it’s such an important phase in software and IT workflow development, and what the benefit is in creating new data connections that will help drive improved collaboration across differing tools and teams.
What is Data Integration?
Data integration’s meaning refers to the process of making organization-wide data from a variety of sources consistent, accurate, up-to-date, and available in a standard format for use in business intelligence, data analytics, and other operational purposes. It involves data replication, data ingestion, and the transformation of data to a common standard of quality for storage in a target repository like a data warehouse, data lake, or data lakehouse.

Data integration definition
How Does Data Integration Work?
Understanding how data integration works is key to understanding its effect on your workforce, workflows, and technology. The more an organization depends on data, the more one place from which data uniformly accesses, stores, and manages data quality becomes increasingly hard to create. There needs to be a defined route built in order to move data easily across systems.
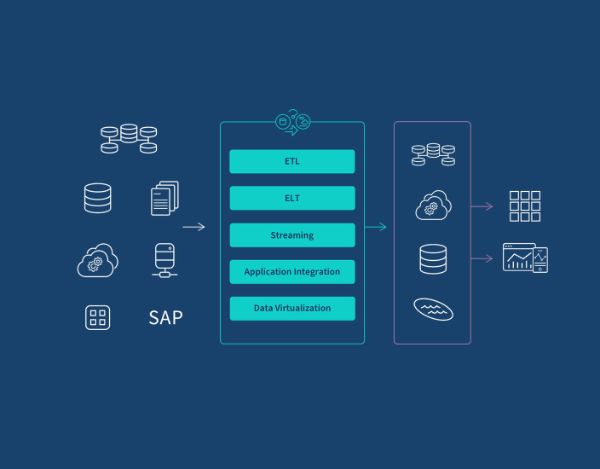
Data integration is a multistage process whereby data from a variety of sources is combined and transformed into one comprehensible format that can be used more generically. Here is an overview of how the workflow for the typical data integration process will go:
Data Source Identification
First comes the identification of all the required data sources to be integrated, including sources like databases, spreadsheets, cloud services, APIs, and legacy systems.
Data Extraction
The extraction tools or processes extract data from these sources, which may involve querying databases, access, and retrieval of files from remote locations, or the collection of data through APIs.
Data Mapping
Since different sources often represent similar information in different ways, in their own codes, terminologies, or structures, there is a need to create a mapping schema that aligns data elements across systems in such a way that consistency during integration is assured.
Data Validation and Quality Control
Validation checks are done to ensure that the data does not have any errors, inconsistencies, or problems in its integrity to make it accurate and qualitative. The processes of quality control in regard to the data are ensured.
Understanding how data integration works
Data Transformation
Structural organization and standardization to ensure homogeneity, accuracy, and compatibility are applied to the extracted data. This may involve cleansing, enrichment, and normalization of data.
Data Loading
On this level, the transformed data is loaded to a target repository-for instance, a data warehouse-where it can be accessed for further analysis or reporting. This can be done either in batch or real-time, depending on the requirement.
Data Synchronization
It is at this stage that mechanisms for data synchronization are implemented to ensure that the data remains updated through edits or by developing real-time integration of new data as may be needed.
Data Governance and Security
Therefore, governance practices are followed in order to keep sensitive or regulated data compliant with the requirements stipulated by the various privacy and regulatory programs. In addition, security controls ensure that the data being integrated and stored does not suffer any integrity compromise.
Metadata Management
Metadata describing integrated data is extremely useful for discoverability and usability, providing context, source information, and details on its structure and purpose.
Data Access and Analysis
Once integrated, the data then becomes available for insight to drive decisions and strategic actions through the use of BI software, analytics platforms, and reporting tools.
This is a summary: Data integration combines technical processes, tools, and best practices to make different data sources harmonious. It ensures data accuracy, availability, and readiness for meaningful analytics that drive informed business decisions.

how to integrate data from multiple sources
Types of Data Integration
There are several ways of integrating data, and each of them has its own set of advantages and limitations. The choice of which one to use would depend on the specific needs of an organization regarding data, the currently existing technological infrastructure, the level of performance desired, and budgetary concerns.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
An ETL pipeline is a traditional data integration method involving three steps: extracting data, transforming it in a staging area, and then loading it into a target repository, often a data warehouse. This approach is optimal for smaller datasets requiring complex transformations, enabling efficient, accurate analysis within the target system.
Change Data Capture: CDC is a kind of variation in ETL wherein it detects changes to a database and captures those changes. These may then be propagated to another repository or even transformed in preparation for ETL, EAI, or other integration tools.
ELT (Extract, Load, Transform)
In the process of ELT, data is loaded directly into the target system-cloud-based data lake, warehouse, or lakehouse-before transformation. This technique applies best when dealing with big datasets in which speed of load is critical. ELT will also run on a micro-batch basis, where only the most recent changes are loaded, or through CDC where for all intents and purposes, continuous syncing occurs in real time as updates occur at the source.
Data Streaming
Data streaming provides the capability to move in real time from source to target by bypassing batch processing. Instead of the need to stage data for loading at a later time, the process of streaming sends the data continuously to support immediate analytics on their data warehouses, data lakes, and any other streaming-ready platforms.

Data integration methods
Application Integration
Application integration involves the connecting of different applications for data synchronization and exchange. This often is an operational necessity. Examples would include HR and finance systems requiring data consistency. Applications have their distinct APIs for data interchange, and SaaS automation tools are available that are offered for creating and maintaining efficient API connections at scale.
Data Virtualization
Data virtualization provides access to the data in real-time, at the exact time desired by the user or application. The definition of virtualization is on-demand access to integrated data obtained through aggregation of information from different systems. Just like streaming, virtualization goes well with transactional systems, where high performance and speed are the imperative in querying.
Benefits of Data Integration
Accompanied with data integration are a lot of advantages in making better decisions, smoothing workflow, and causing competitive advantage. Core benefits accruable include:
Improved Data Quality and Credibility
Data integration ensures that no guessing games around KPIs are made, nor any stakeholder has to deal with inconsistent or unreliable data. This is because information is placed in one place for truth, cuts down on errors, reworks, and gives one common source of truth that everybody can look upon and lean on.
Improved Collaboration and Data-Driven Decisions
When raw data and data silos are transformed into unified, analysis-ready information, team members across the organization are sure to evince more interest in data analysis. This also allows for cross-departmental collaboration because unified data gives a clear overview, further helping teams make out how their role is influencing and affecting other teams.

Data integration improved collaboration and data-driven decisions
More Efficiency
Data integration, in turn, enables analysts, developers, and IT professionals to focus resources on priority projects rather than wasting them by manually collecting and preparing data or developing a one time connection with custom reports. Efficiency liberates teams to invest more energy in strategic initiatives that drive business value.
Popular Data Integration Tools
Data integration tools are software solutions intended for ingesting, consolidating, transforming, and transferring data from its source to a specified destination. These tools also perform other essential tasks necessary for the quality of data, such as data mapping and cleaning.
The correct tool will facilitate your integration process. However, it is important to identify the key features that typify a good integration tool. The following are the key attributes that you need to look out for:
- User-Friendly Interface: The tool should be intuitive and lightweight to use, minimizing the learning curve for your team.
- Extensive Pre-Built Connectors: Whenever possible, look for tools that boast high numbers of pre-built connectors to suit a broad range of data sources.
- Open Source Flexibility: Open source options are much more flexible and offer greater customization potential.
- Portability: It should allow data to move seamlessly between environments when needed.
- Cloud Compatibility: Cloud capabilities ensure that integrations are supported at any scale, and also accessible at varied levels in your organization.
Until recently, the traditional way of integrating data has been by hand-coding of scripts in SQL, which has always been the standard programming language for relational databases.

Data integration tools
Today, a variety of IT providers offers various types of data integration tools: open-source solutions or platforms that automate the integration process in an efficient and well-documented way. Typically, all different types of data integration tool solutions will include a few of the following components:
ETL Tools
ETL-Extract, Transform, and Load-develop tools that will enable the extraction of data from various sources, transform them into needed formats, and load into target systems, including databases and data warehouses. These tools are not only used for data warehousing purposes but also in general have huge usage in data integration and migration.
Enterprise Service Bus and Middleware
These tools can facilitate integration among different software applications and services through a messaging and communication framework. Real-time exchange, workflow orchestration, and API management are supported.
Data Replication Tools
These enable the replication of data continuously from source systems to target systems for synchronization. They find their application in scenarios like real-time data integration, disaster recovery, and high availability maintenance.
Data Virtualization Tools
Data virtualization provides a unified view of data from diverse sources through the development of a virtual layer, in which its reality is kept abstract-the actual physical location of the data is elsewhere. It may also include things like access to and querying of integrated data, all without its actual physical movement.
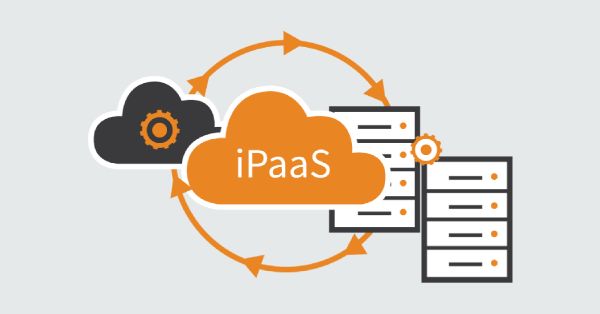
Integration Platforms as a Service (iPaaS)
The iPaaS solutions provide integration of data in the cloud, offering various services like data transformation, routing, API management, and connecting with cloud and on-premise applications. They find their application mainly in integrating hybrid clouds and SaaS applications.
The iPaaS solutions provide integration of data in the cloud
Streaming Data Integration Tools
These tools have specialized focuses on the real-time integration of streaming data from sources like IoT devices, sensors, social media, and event streams. In general, these tools will let organizations process and analyze data in real time, as it is created.
Data Quality and Governance Tools
These tools are responsible for guaranteeing that data brought from various sources has quality standards and regulatory compliance, with support for data governance policies. Additional functionality may include data profiling, cleansing, and metadata management.
Change Data Capture Tools
CDC tools monitor and propagate all the changes happening in data at source systems in real time. They are being used quite often nowadays to keep data warehouses up-to-date and to perform real-time analytics.
Master Data Management Tools
The tools used by MDM mainly focus on the critical type of data including customer, product, and employee data for its consistency and accuracy. Most of the tools have data integration features to consolidate the coming master data from different systems.
API Management Platforms
Some of these online platforms can be used to design, publish, and manage APIs. Although the main task being carried on these platforms is the integration of APIs, they work effectively as a bridge between the different systems and applications.
Challenges in Data Integration
One of the major challenges in the integration of data within existing systems is the interoperability of a wide range of systems to create a unified system. This may cause a number of issues, including but not limited to:
Difficulty in Locating Data Quickly
If this data is not available, teams end up spending hours tracking what they are looking for, which holds them back in terms of productivity. Other times, some groups don’t even have access to important data that would have most likely provided insight into better strategy buildups.
Challenges in data integration
Low-Quality or Outdated Data
In continuous data gathering, an organization sometimes acquires huge volumes of information. Without appropriate standards for data entry, this information may be inaccurate, outdated, redundant, or incomplete. Solutions for data standardization and structuring are highly required for such inconsistencies.
Data coupled with other applications
When data is buried in or becomes dependent on specific applications-especially older and legacy systems-it is difficult to apply outside of those applications in question, hence stunting flexibility and scalability.
Inconsistent Formats and Sources
With several departments participating, different applications for their activities-a couple of examples being sales, marketing, and customer support-data format can also vary, causing inconsistencies. Even minor differences in how any given data field is formatted-for instance, the formatting of a telephone number-can cause misalignment of data and, therefore, integration issues.
Using Ineffective Software Solutions
One is stuck with an integration tool, which by no ways guarantees whether it is the right one or being used properly. The necessary capabilities from a data integration solution are to be judged and ensured whether it is being utilized in the best manner to achieve those demands.
Overwhelming Volume of Data
Too much information is sometimes just that. And without any strategy, one may accumulate data for which, in fact, there is no real plan to analyze it, when that meaningful information might be buried under unnecessary data.
Too big volume of data causes difficulty for data integration
Key TakeAways
In today’s data-driven landscape, data integration is essential for businesses aiming to harness the full potential of their information assets. It is all about the harmonious integration of data coming from different sources into a unified consistent view that enables organizations to make better decisions, gain operational efficiency, and ensure coordination at an interdepartmental level. Such integration of fragmented data sets enables companies to avoid silos; ensure accuracy in data; and fosters a culture of decision-making based on data.
As such, data integration strategies will be of paramount importance for those organizations intending to enjoy a competitive advantage. Automation of processes and the provision of more complete data in a timely manner to employees enable companies to quickly respond to market demands and customer needs for agility in growth and innovation.
If your organization wants to upgrade its functionality in terms of data integration, explore solutions such as those offered by Byte Pilot. At Byte Pilot, your business is taken through the maze of integrating data, with big data processing and data integration services, to ensure that the right tools and strategies are in place for converting data into actionable insights. Let data integration move your organization toward new opportunities and possibilities that will lead to success.